Spin Current Generation by Edge Plasmons in Graphene Ribbons
Abstract ---
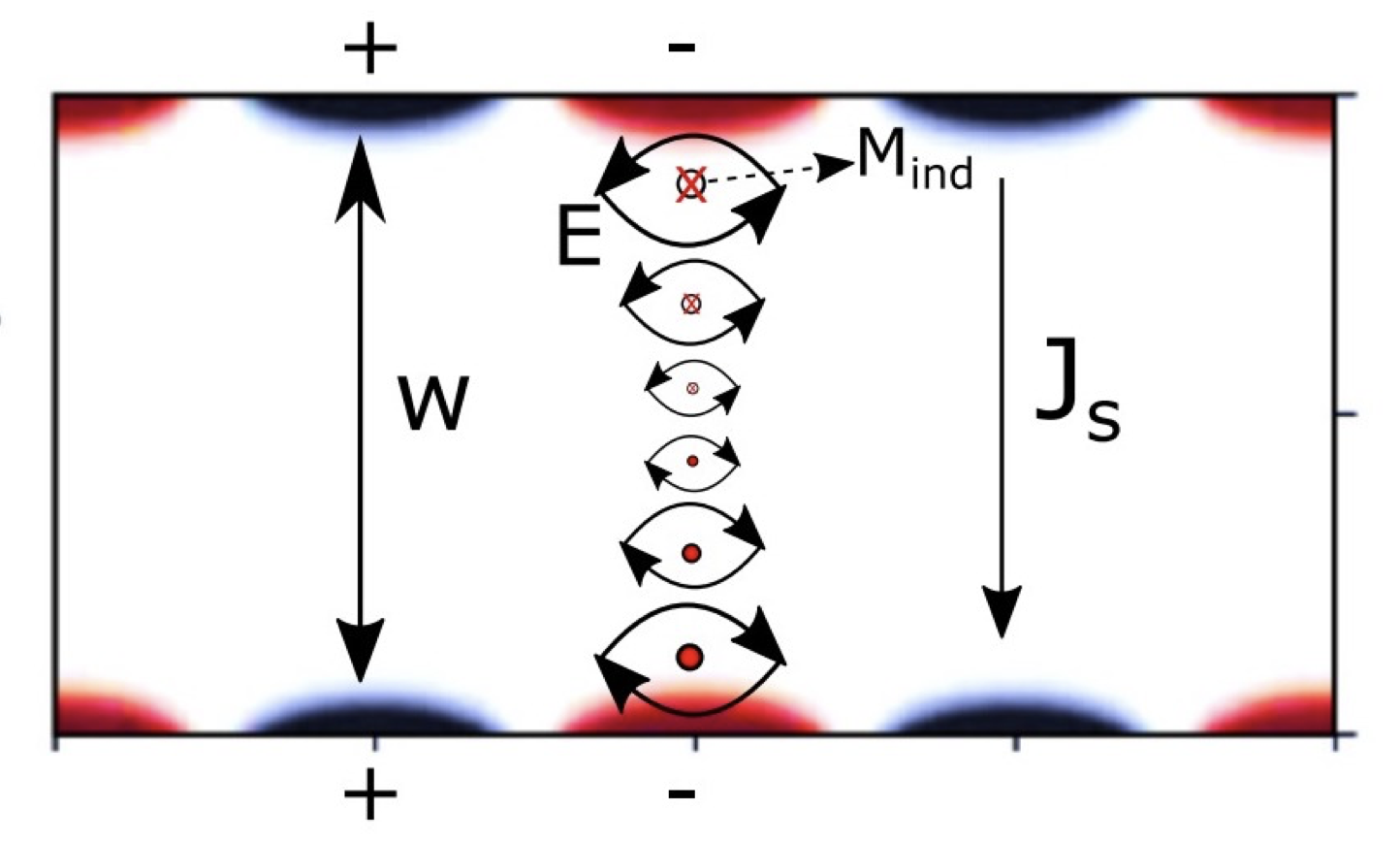
We discuss the generation of a spin current by an edge plasmon in a
graphene ribbon, which is a kind of surface plasmon that is localized
near the edges of the ribbon. In contrast with a surface plasmon on the
surface of a three-dimensional metal, the electric field of the edge
plasmon rotates as a function of the time in the plane of graphene,
which means that the optical spin-angular momentum of the edge plasmon is
out of plane. We found that the electric-field-induced spin current
flows by the inverse Faraday effect between the edges of the ribbon with
spin polarization of electrons in the out-of-plane direction.
The symmetric mode of the edge plasmon gives a larger magnitude of
the spin current than the antisymmetric mode does. Moreover, the
magnitude and direction of the spin current are tunable not only by the
frequency of the edge plasmon, but also by the Fermi energy of graphene,
which enables application to a spin-switching device controlled by
a gate voltage.
Phys. Rev. B 103, 245428 (2021)
Back to Publications